Learning SQL queries
In this tutorial you’ll learn:
- The key integrity constraints in a relational database.
- Basic SQL queries.
1 Description of the data
We consider the database of a DVD rental store chain containing data on films, actors, customers and the transactions of the store.
This database goes by the name Sakila and was developed by Mike Hillyer, a former member of the MySQL team.
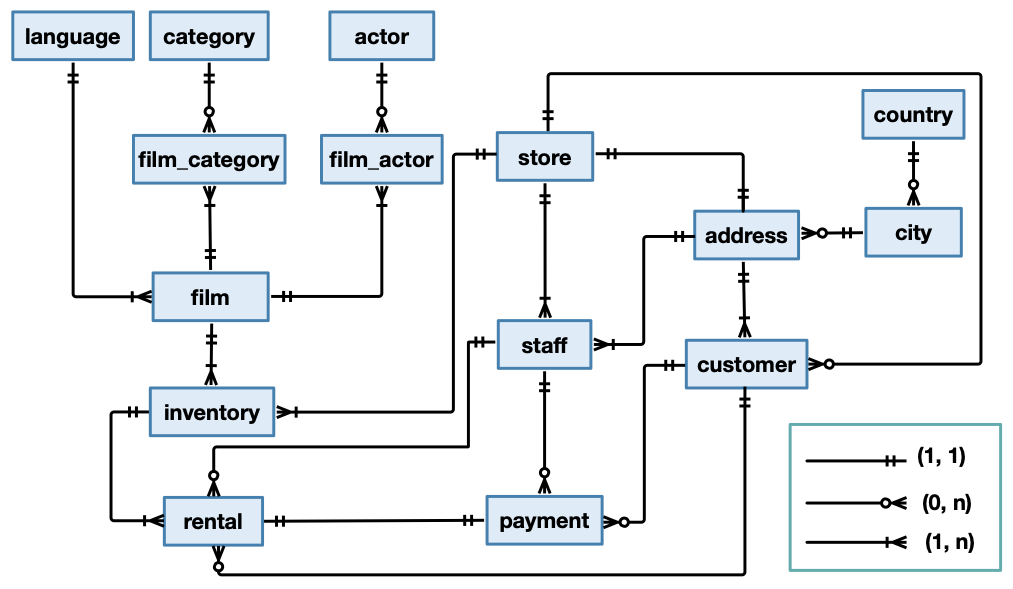
Figure 1.1: The conceptual schema of the Sakila database
The tables of the database are documented on this page.
Sakila has been ported from MySQL to PostgreSQL under the name pagila. In pgAdmin, Open a new query tool to do the exercises.
2 Integrity constraints
Exercise
Exercise 2.1 Execute the following statement:
insert into film_actor (actor_id, film_id) values(1, 25)
What is this statement supposed to do? What is the reaction of the DBMS?
Exercise
Exercise 2.2 Write the statement to delete the film with film_id=1 from the table Film.
Execute the command. What happens?
Exercise
Exercise 2.3 Look at the definition of the foreign key constraints in table film_actor (see in the Database structure tab).
Is the definition of the foreign key constraint to table film coherent with the behavior observed in the previous exercise?
Exercise
Exercise 2.4 Execute the following query:
SELECT f.film_id as film_id_in_table_film,
fa.film_id AS film_id_in_table_film_actor,
fa.actor_id as actor_id, f.title as title
FROM film f JOIN film_actor fa USING (film_id)
WHERE f.title='ACE GOLDFINGER'
What does the query? Note down the identifier of the film in both tables film and film_actor. (columns film_id_in_table_film and film_id_in_table_film_actor).
Exercise
Exercise 2.5 Write and execute a statement to set the value 10000 to the identifier of the film ACE GOLDFINGER in table Film.
After the modification, execute the query of the previous exercise. What changed? Explain in details what happened.
Exercise
Exercise 2.6 Execute the following statement:
UPDATE film_actor SET film_id=2 WHERE film_id=10000
What does it? What happens? Explain.
3 Basic queries
Exercise
Exercise 3.1 Write the following SQL queries:
Return all the information on all customers.
Return the first and last name of all customers.
Return the first and last name of all customers of the store with identifier 1.
4 Sorting and paginating
Exercise
Exercise 4.1 Write the following SQL queries:
Return the last and first name of all customers. Sort by last name in ascending order.
Same as in 1., but only return the first 100 customers.
Return the last and first name of all customers of the store with identifier 1. Sort by last name in ascending order and by first name in descending order.
5 Aggregating queries
Exercise
Exercise 5.1 Write the following SQL queries:
Count the number of films in the database (expected result: 1000).
How many distinct actor last names are there?
Compute the total amount of payments across all rentals (expected result: 67416.51).
Compute the average, minimum and maximum duration of rental across all films (expected result: 4 days 24:36:28.541706, 18:00:00, 9 days 05:59:00).
Return the number of actors for each film.
Return the number of copies of each film in each store (table inventory).
Same as 6., but only returns the pairs (film, store) if the number of copies is greater than or equal to 3.
6 Join queries
Exercise
Exercise 6.1 Write the following SQL queries:
Return the first and last name of the manager of the store with identifier 1 (expected result: Mike Hillyer).
Return the first and last name of the actors in the film ACE GOLDFINGER.
Return first and last name of each actor and the number of films in which they played a role.
Same as in 3., but order by number of films in descending order.
Same as in 4., but only return actors who played a role in at least 10 films.
Return the identifier, the first and family name of the customers who have rented between 5 and 10 movies in the category Family.